The uptick in technology and a digital-first approach to business provides many benefits. However, it also creates opportunities for increasing cybercrime. Application security is constantly developing as an essential component of any organization, and companies are discovering the ways investing in a robust application security stack, for instance, DAST coupled with penetration testing, can help protect business-critical assets.
DAST and pentesting both have the same goal to minimize risk and prevent attacks before they happen. Yet, the two approaches have notable differences that businesses should take into account.
What’s the difference between DAST and pentesting?
DAST automates a simulation of attacks by using programmatic screening tools, while modern pentesting is a mainly manual testing process by trained security experts (pentesters) to test an asset's security.
Understanding the differences of these two security approaches is an important start but how can your organization leverage these differences?
DAST vs Pentesting
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is a simulation of automated attacks during runtime. That’s where the “dynamic” aspect comes into play, as it functions while systems are already running. Further, DAST is a fully automated process using screening tools which differs from pentesting which relies more on human testing. This makes DAST tools more ideal for frequent scans and pentesting better for a more in-depth view of your asset's security. Explore other benefits of pairing penetration testing and DAST.
DAST Screening Tools
DAST tools perform a black-box test that communicates with a web application to identify potential security vulnerabilities and weaknesses. These screening tools are good for pinpointing a variety of security risks, including:
- Cross-site scripting
- SQL injection
- Command injection
- Insecure server configuration
- SSRF
However, “DAST also has limited effectiveness in the detecting of non-reflective attacks (i.e – XSS) and other design flaws (coding errors) that can lead to stability issues.” (The CyberSecurity Place)
Pentesting and PtaaS
Pentesting is a proactive cybersecurity practice defined as, “a method of testing where testers target individual binary components or the application as a whole to determine whether intra or inter component vulnerabilities can be exploited to compromise the application, its data, or its environmental resources.” (CSRC)
Penetration testing applies targeted attacks from trained cybersecurity professionals, where testers identify potential vulnerabilities and report detailed findings that companies can leverage for remediation. It also offers a different view of your security posture compared to DAST tools which often miss business logic, chained exploits, and more.
Traditional one-off pentesting rarely focuses on speed, automation and agility, leading to delays in the release cycle and more. To keep up with modern technology and business security practices, pentesting has begun evolving into Pentest as a Service (PtaaS). PtaaS is focused on testing for heightened security, speed, and affordability, differing from traditional pentesting by providing a modernized cloud-based platform with software integrations and automatic reporting.
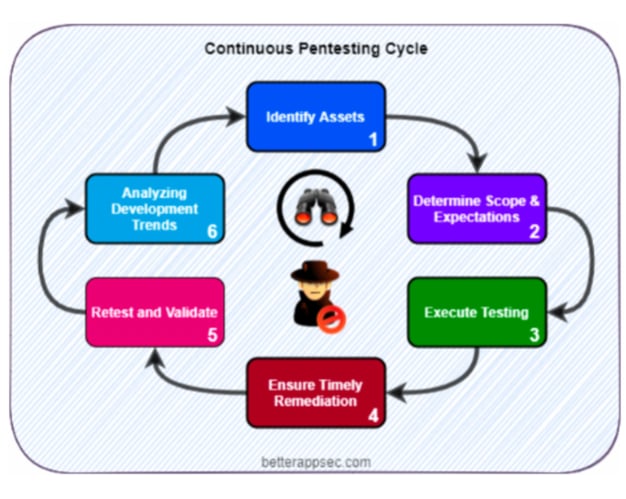
A continuous pentest program ensures that the assets that are most business critical are regularly tested. This way, there is a much higher likelihood that high-risk vulnerabilities will be identified and remediated quickly. What is your DAST tool missing? The benefits of integrating a Pentest as a Service platform. Learn more about the benefits PtaaS can bring to your organization.