In cybersecurity, strategies are broadly divided into two categories: offensive and defensive. While both approaches are vital, they offer different perspectives on protecting, detecting, and responding to threats.
The key is employing the right strategy at the right time in order to protect against attackers, maintain business continuity in the face of cyberattacks, optimize resources, and adhere to regulatory compliance.
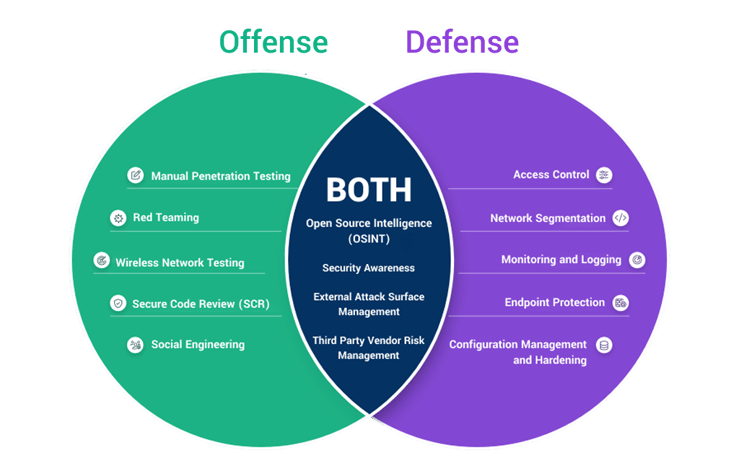
What is Offensive Cybersecurity?
Offensive cybersecurity, commonly called "OffSec," focuses on actively seeking out systems' vulnerabilities, flaws, and weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. The premise behind OffSec is simple: to best defend oneself, one must think and act like an attacker.
This proactive approach includes strategies like penetration testing (or pentesting), red teaming, phishing simulations, and vulnerability assessments.
Offensive Cybersecurity Tools and Technologies
Penetration Testing Tools
- Metasploit: One of the most popular penetration testing frameworks, it helps in discovering, exploiting, and validating vulnerabilities.
- Burp Suite: Widely used for vulnerability scanning and application security testing.
Vulnerability Assessment
- Nessus: A well-known vulnerability scanner tool.
- OpenVAS: An open-source vulnerability scanning and management software.
Phishing Simulation
- GoPhish: An open-source phishing toolkit designed for businesses and penetration testers.
- Phishing Frenzy: An open-source Ruby on Rails application leveraged by penetration testers for managing email campaigns.
Red Teaming Tools
- Cobalt Strike: Offers post-exploitation capabilities and network operations for red teams and adversaries.
- Empire: A post-exploitation agent built on crypto logically-secure communications.
Steps Toward And Offensive Security Strategy
To ensure an OffSec program's success and relevancy, organizations must:
- Define the Scope and Set Targets: Clearly define what systems, networks, or applications will be assessed. This may vary based on company size, industry, or regulatory demands.
- Pinpoint Key Data and Systems: Determine which assets would have the highest impact on the organization if they were to be compromised.
- Define Success Metrics and Measure Outcomes: These could range from the number of vulnerabilities detected to the effectiveness or timing of incident response during simulations.
- Integrate OffSec with Defensive Strategies: Ensure that findings from offensive exercises feed into the company's defensive strategy to improve its cybersecurity.
What is Defensive Cybersecurity?
While offensive cybersecurity aims to identify vulnerabilities by actively simulating cyberattacks, defensive cybersecurity, or "DefSec," focuses on building and maintaining resilient systems that can prevent, detect, and respond to threats as they arise.
This approach emphasizes layers of protection, including firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and incident response teams. The primary goal is to prevent, detect, and mitigate threats.
Defensive Cybersecurity Tools and Technologies
Firewalls
- Cisco ASA: A security device that combines firewall, antivirus, intrusion prevention, and virtual private network (VPN) capabilities.
- pfSense: An open-source firewall and router that is also feature-rich.
Antivirus Software
- Symantec Endpoint Protection: Provides malware protection, threat intelligence, and more.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security: Offers advanced threat defense, ransomware protection, and risk and vulnerability assessment.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Snort: An open-source network intrusion detection and prevention system.
- Suricata: A high-performance Network IDS, IPS, and Network Security Monitoring (NSM) engine.
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
- Cisco Firepower: Known for its threat-focused next-generation IPS.
- Fortinet FortiGate: Offers both Firewall and IPS capabilities.
Incident Response Tools
- TheHive: A scalable, open-source, and free Security Incident Response Platform.
- MISP (Malware Information Sharing Platform & Threat Sharing): Used for gathering, sharing, storing, and correlating Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) of targeted attacks.
Employee Training Platforms
- KnowBe4: Provides security awareness training for employees to recognize and handle phishing attacks, ransomware attacks, and other cyber threats.
- Infosec IQ: Offers a security awareness and training platform to reduce human error and drive change.
How to Establish Goals for a Defensive Security Program
- Asset Identification: Start by recognizing which assets are critical and require protection. This includes understanding where sensitive data resides and how it moves within and outside the organization.
- Threat Modeling: Understand the potential threats facing the organization and design defenses accordingly.
- Develop a Layered Defense Strategy: Often referred to as defense-in-depth, this involves multiple layers of security controls and measures to protect data.
- Create an Incident Response Plan: Ensure that, in the event of a security breach, there are established procedures to mitigate damage, recover compromised data, and restore system integrity.
- Training and Awareness: Ensure that all employees know potential security threats, how to recognize them, and how to report them. Regular training ensures that the human element is also a robust line of defense.
Defensive security strategies provide continuous protection against a broad spectrum of threats and maintain the integrity of data, keeping it consistent and reliable throughout its lifecycle. They also help facilitate adherence to industry regulations, minimizing legal and compliance risks.
By preventing or mitigating the effects of breaches, DefSec reduces potential business disruptions. In tandem with offensive cybersecurity measures, defensive strategies form a comprehensive, resilient approach to safeguarding an organization's digital assets and reputation.
OffSec and DefSec: Why Both Matter
The relationship between OffSec and DefSec is a balance between attack and defense. OffSec focuses on pinpointing gaps and weaknesses, while DefSec works to address and strengthen those vulnerabilities.
- Shared Intelligence: A robust security program intertwines both strategies. Information gleaned from penetration tests or red teaming exercises (OffSec) should guide the fortification of defense systems.
- Dynamic Defense through Offense: A strong offense can provide the insight needed to bolster defensive strategies. By understanding attacker TTPs, DefSec can better predict and mitigate future attacks.
- Proactive vs. Reactive Mindset: OffSec tends to be more proactive, seeking out vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. DefSec, however, often operates reactively, responding to threats as they arise. A balance ensures that the organization can anticipate threats while also being ready to respond to unexpected challenges.
Finding the Right Mix
OffSec is all about identifying vulnerabilities—spotting the weak spots in systems before attackers do. This strategy provides invaluable data about potential weak points in an organization's digital armor. Meanwhile, DefSec takes on the role of protection, using the intelligence provided by offensive operations to reinforce these vulnerabilities.
When a vulnerability is found, defensive strategies are updated to address these specific concerns. In essence, knowing the attackers' tactics, techniques, and procedures allows for a more targeted defensive approach. This synergy ensures organizations are not only shielded but also consistently adapt to the dynamic world of cyber threats.
For organizations, striking the right balance between OffSec and DefSec might depend on several factors:
- Risk Appetite: Companies in high-risk sectors like finance or healthcare might lean more heavily into OffSec to proactively uncover and patch vulnerabilities.
- Resource Availability: Depending on budget, staffing, and technical expertise, an organization might lean towards one strategy over the other. However, third-party vendors and cybersecurity firms can bridge these gaps.
- Regulatory and Compliance Needs: Some industries are bound by strict regulations that dictate specific defensive controls. In such cases, DefSec would naturally take precedence.
Towards a Holistic Security Posture
Cybersecurity is not a zero-sum game. Offensive doesn’t diminish the importance of defense, and vice versa. Both have their roles and benefits:
- Innovation and Adaptation: OffSec activities like pentesting push the boundaries and often lead to discovering novel vulnerabilities or attack techniques. This, in turn, promotes innovation in the DefSec realm.
- Deterrence through Defense: A well-fortified defense protects an organization and can act as a deterrent. When attackers face significant barriers, they might deem the target too resource-intensive and move to easier prey.
- Awareness and Culture: OffSec activities like phishing simulations raise employee awareness, fostering a security-conscious culture. This human aspect complements the technical defenses in place.
Embracing An Integrated Approach to Cyber Safety
In the evolving landscape of cyber threats, a one-size-fits-all strategy does not exist. By understanding the unique strengths and applications of both offensive and defensive tactics, organizations can craft a tailored, multi-faceted approach to cybersecurity.
This holistic stance ensures not only protection from current threats but also preparation for the challenges of tomorrow.
Learn more about how Offensive Security can help improve your security posture by contacting Cobalt today!
FAQ
Offensive cybersecurity, also called "OffSec," focuses on proactively finding vulnerabilities in systems before attackers can exploit them. It involves thinking like an attacker to identify weaknesses.
Some strategies used in offensive cybersecurity include:
- Penetration testing (pentesting)
- Red teaming
- Phishing simulations
- Vulnerability assessments
Cobalt offers a variety of services related to offensive security, including application pentesting, network pentesting, and cloud security.
Defensive cybersecurity focuses on creating and maintaining secure systems that can prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats. It emphasizes layered protection to safeguard systems and data.
Some common strategies used in defensive cybersecurity include:
- Asset Identification: This involves figuring out which assets are the most important and need protection. It also includes knowing where sensitive data is stored and how it moves within and outside the organization.
- Threat Modeling: In this step, organizations try to understand the possible threats they might face and then design defenses accordingly.
- Developing a Layered Defense Strategy: This strategy, often called "defense-in-depth," uses multiple layers of security controls and measures to protect data.
- Creating an Incident Response Plan: It's crucial to have set procedures in place to reduce damage, recover lost data, and restore systems if a security breach occurs.
- Training and Awareness: Organizations need to make sure all employees understand potential security threats, how to spot them, and how to report them. Regular training helps turn the human element into a strong line of defense.
Both offensive and defensive cybersecurity are crucial for a comprehensive security approach. Offensive cybersecurity helps identify vulnerabilities, while defensive cybersecurity uses that information to strengthen defenses and protect systems.They work together to provide a complete and adaptable cybersecurity strategy.








